Omega-3s for Vegetarians: How to Get Your Daily Dose Without Fish
When we think of Omega-3s, fish like salmon and sardines usually come to mind. But what if you don’t eat fish? No worries—you’re not missing out.
While fish provide direct sources of EPA and DHA (the most beneficial Omega-3s), vegetarians can still get plenty of Omega-3 from plants, mainly in the form of ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). The body can convert ALA into EPA and DHA, but the process is slow, so vegetarians need to be mindful about what they eat.
Why Omega-3s Matter
Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation, support heart and brain health, and help keep your skin and hormones balanced.
There are three types:
-
ALA – found in plants, most accessible for vegetarians
-
EPA & DHA – mostly in fish and algae, vital for brain and heart
Since conversion from ALA to EPA/DHA is low, vegetarians should focus on rich ALA sources and consider algae-based supplements.
Top Vegetarian Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids

Now, let us do an inventory of the richest plant-based sources of omega-3s, what their ALA content is, and why they matter.
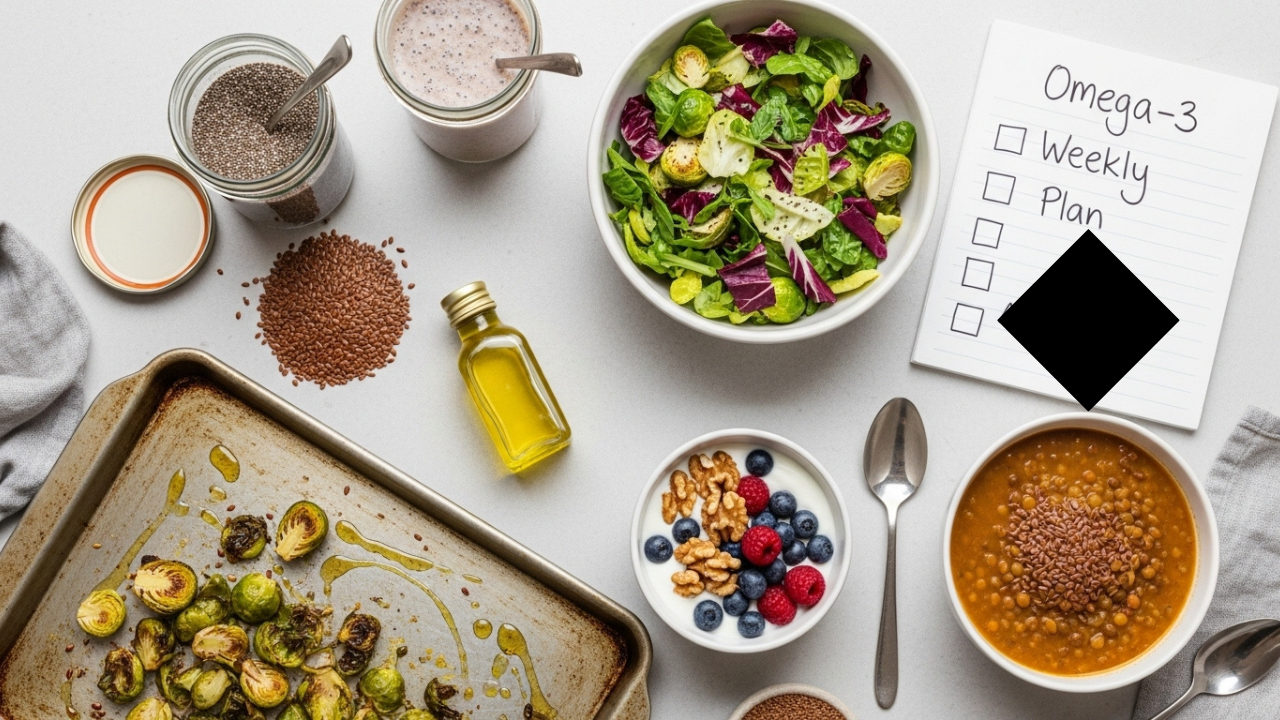
1. Flaxseeds
Flaxseeds are the monarch of ALA omega-3s.
Two to three tablespoons of ground flaxseed contains an ALA dose of approximately 2,350 mg.
Whole flaxseeds often pass through the intestines without absorption.
Ground flaxseed is far superior.
Put in:
- Morning oats
- Smoothies
- Energy balls prepared by hand
- Baked goods
2. Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are tiny giants.
They contain ALA of more or less 2,400 mg per tablespoon, and offer fibre, protein, and antioxidants too.
When left in a liquid, they swell up — making them very good for digestion.
Test them in:
- Chia puddings
- Overnight oats
- Lemon water or juice-style smoothies
- Yogurt bowls
3. Walnuts
One ounce of walnuts offers 2,500 mg of ALA.
They’re heart- and brain-friendly, with antioxidants and vitamin E.
Use them:
- As a snack
- In oatmeal
- In salads
- Crunched on desserts
4. Hemp Seeds
These creamy, crunchy seeds contain about 1,000 mg ALA per tablespoon, plus all nine essential amino acids — a rare quality in plant proteins!
Great in:
- Smoothies
- Grain bowls
- Soups or salads
5. Algal Oil
Although not a true food, algal oil is a vegetarian source of DHA and EPA, produced by extracting marine algae.
It eliminates the need for ALA conversion and is ideal for people who need cognitive or prenatal support.
Available as:
- Capsules
- Liquid drops
Comparison of Omega-3 ALA Content in Common Vegetarian Sources
| Food Source | ALA per tbsp (approx.) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Ground Flaxseed | 2,350 mg | Best absorbed in ground form |
| Chia Seeds | 2,400 mg | Also rich in calcium and fibre |
| Walnuts (1 oz) | 2,500 mg | Anti-inflammatory and heart-healthy |
| Hemp Seeds | 1,000 mg | Complete plant protein |
| Algal Oil (1 tsp) | 400–500 mg DHA & EPA | Direct source of long-chain omega-3 |
Practical Ways to Add Omega-3s into Your Day
- 1 tbsp of ground flaxseed – Ohio State University recommends adding it to a smoothie or mixing it into the batter of pancakes.
- Chia pudding – Place almond milk with vanilla and stir in chia seeds, and leave overnight.
- Simple snack – Eat a handful of walnuts together with an apple.
- Avocado toast upgrade – Sprinkle hemp seed on top.
- Protein-rich stir fry – Add tofu or tempeh to vegetables for a dinner that’s omega-3-friendly.
At each meal, you are not expected to get it right.
The focus is on everyday consumption and alternating your sources.
Why Algal Oil Matters
This is why plant-based nutritionists often recommend introducing an algal oil supplement into vegetarian diets — particularly for:
- Pregnant women
- Individuals with inflammatory conditions
- Anyone with high omega-3 demands
Natural Ways to Take More Omega-3

Here are simple, natural steps to boost your omega-3 intake without radically changing how you eat:
- Make homemade salad dressings using flaxseed oil
- Store chia gel in the fridge and stir it into smoothies or drinks
- Roast Brussels sprouts and coat them with hemp oil for flavor and fats
- Add walnuts to breakfast cereal or yogurt
- Mix ground flaxseed into stews or lentil soups
- Meal prep with awareness — weekly check-ins help track omega-3 variety
Who Should Consider Algal Oil?
While many vegetarians can thrive without direct DHA or EPA, some people benefit more from supplementation — notably:
- Expectant and lactating mothers
- Vegetarian or vegan children
- Older adults with cognitive concerns
- People with depression, mood disorders, or chronic inflammation
Algal oil is the only vegan supplement that contains bioavailable DHA and EPA.
It’s marine-free, well-tolerated, sustainable, and lacks the mercury risk that comes with fish oils.
Summary
Omega-3s are not exclusive to fish.
Nature offers powerful plant-based sources of ALA, and with a little creativity and intention, vegetarians can meet their needs fully.
- Rotate your omega-3 sources
- Control your omega-6 intake
- Be strategic about using algal oil if needed
With long-term consistency, your brain, heart, skin, and hormones will jump with joy.















Leave a Reply